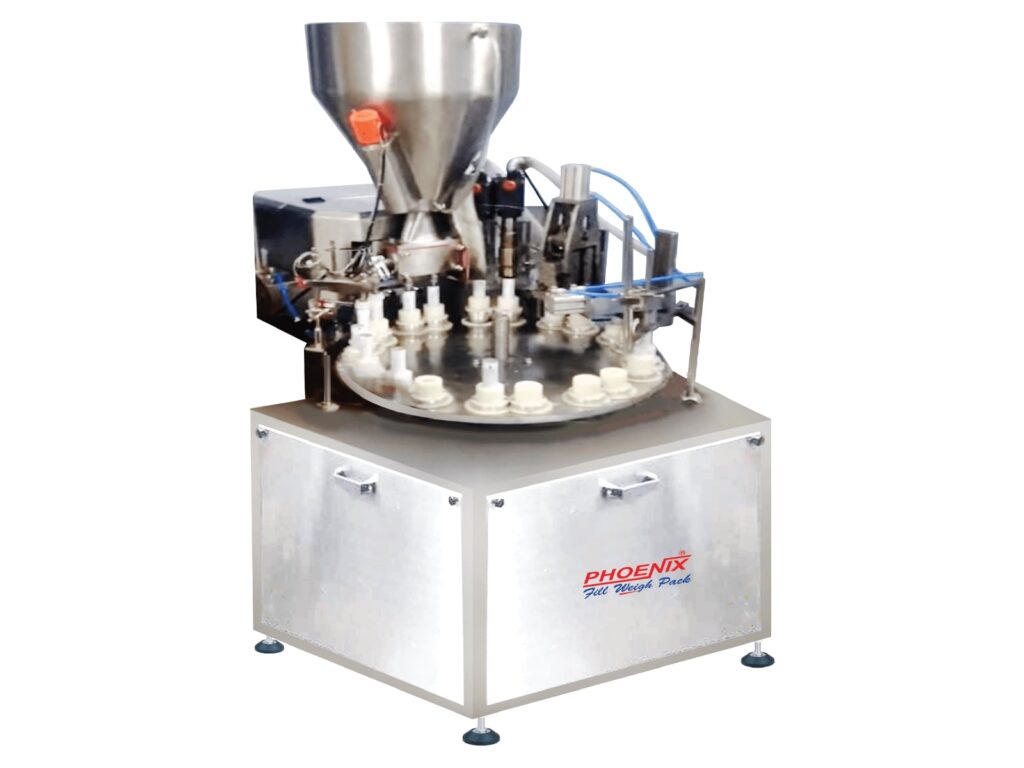
Understanding tube materials is essential for manufacturers and consumers alike. Whether you’re designing products, selecting packaging, or working with a tube filling machine, knowing the differences between plastic, aluminum, and laminated tubes can significantly impact your decision-making process. This guide explores the unique characteristics, advantages, and applications of each material type to help you make informed choices.
Why Tube Materials Matter
Tubes are fundamental components in various industries—from cosmetics and pharmaceuticals to adhesives and personal care products. The material you choose affects product quality, shelf life, sustainability, and manufacturing efficiency. When operating a tube filling machine, the material compatibility becomes even more critical, as different tubes require specific handling, filling speeds, and sealing methods.
The choice between plastic, aluminum, and laminated materials isn’t just about cost; it’s about finding the perfect balance between protection, functionality, and environmental impact.
Plastic Tubes: Lightweight and Versatile
Characteristics
Plastic tubes, typically made from polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), or polyethylene terephthalate (PET), are the most commonly used packaging solution in the market. They’re lightweight, affordable, and offer excellent design flexibility with custom colors, shapes, and printing options.
- Lightweight and easy to handle during production
- Cost-effective compared to other materials
- Excellent graphics and branding capabilities
- Variety of closure options available
- Good moisture barrier in PET variants
Best Applications
Plastic tubes excel in cosmetics, skincare products, and toiletries. They’re ideal for products that don’t require extensive light protection or extremely long shelf life. Many tube filling machine setups are optimized for plastic tube processing due to their ease of handling and cost-efficiency in high-volume production runs.
Considerations
The primary drawbacks include sensitivity to certain aggressive chemicals, limited barrier properties for sensitive products, and environmental concerns. Plastic tubes are susceptible to oxygen and moisture permeation, making them less suitable for pharmaceutical-grade products or items requiring extended stability.
Aluminum Tubes: Premium Protection and Longevity
Characteristics
Aluminum tubes provide superior protection and have been a gold standard in pharmaceutical and premium cosmetic packaging for decades. Made from pure aluminum or aluminum alloys, these tubes offer exceptional barrier properties and durability.
- Complete light barrier—protects photosensitive products
- Excellent oxygen and moisture barrier
- Premium appearance and perceived value
- Temperature stable and chemically inert
- Fully recyclable and sustainable
- Extended shelf life for sensitive formulations
Best Applications
Aluminum tubes are preferred for pharmaceuticals, high-end cosmetics, sunscreens, and products requiring maximum stability. They’re particularly valuable in pharmaceutical manufacturing where product integrity and shelf life are non-negotiable. Many advanced tube filling machine systems are designed specifically to handle aluminum tubes, offering precise filling and sealing capabilities.
Considerations
The main disadvantages are higher costs and increased environmental impact during production. Aluminum tubes also require protective lacquer coating to prevent internal corrosion from reactive ingredients, adding complexity to manufacturing. Additionally, they offer less design flexibility for vibrant graphics compared to plastic alternatives.
Laminated Tubes: The Hybrid Solution
Characteristics
Laminated tubes combine multiple materials—typically plastic, aluminum foil, and plastic layers—to create a hybrid packaging solution. This innovative structure provides many benefits of aluminum with improved flexibility and design options.
- Excellent barrier properties comparable to aluminum
- Better design and branding flexibility than aluminum
- Lighter weight than full aluminum tubes
- Cost-effective middle ground between plastic and aluminum
- Improved chemical resistance
- Extended product shelf life
Best Applications
Laminated tubes are increasingly popular in cosmetics, personal care, and specialty pharmaceutical products. They offer the protective benefits needed for sensitive formulations while maintaining the aesthetic appeal of branding. Modern tube filling machine technology has adapted well to laminated tubes, making them an attractive choice for manufacturers seeking performance and economics balance.
Considerations
The main challenge with laminated tubes is recycling complexity—the multiple material layers make them more difficult to process in standard recycling streams. They also require specialized equipment for proper filling and sealing compared to single-material tubes.
Comparative Overview
| Property | Plastic | Aluminum | Laminated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Low | High | Medium |
| Barrier Properties | Fair to Good | Excellent | Excellent |
| Design Flexibility | Excellent | Limited | Very Good |
| Weight | Light | Moderate | Light to Moderate |
| Shelf Life | 6-12 months | 3+ years | 2-3 years |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate to High | Low (recyclable) | Moderate |
| Recyclability | Easy | Easy | Difficult |
Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
Choosing the ideal tube material depends on several factors: product formulation and stability requirements, shelf life expectations, target market and pricing strategy, branding and aesthetic needs, production volume and equipment compatibility, and environmental considerations.
For Budget-Conscious Brands
Plastic tubes are your best choice. They offer cost efficiency and adequate protection for products with moderate shelf life requirements. Ensure your production equipment, particularly your tube filling machine, is calibrated for proper filling to maintain product quality.
For Premium and Pharmaceutical Products
Aluminum tubes provide unmatched protection. The investment in premium packaging justifies the higher cost for products where stability and shelf life are critical success factors.
For Balanced Requirements
Laminated tubes offer an excellent compromise, providing strong barrier properties with better economics and design flexibility than aluminum alone.
Manufacturing Considerations
Modern tube filling machine systems must accommodate different tube types. Each material has unique handling requirements: plastic tubes need moderate pressure for filling, aluminum tubes require precise sealing to avoid deformation, and laminated tubes demand careful temperature control during sealing operations. Investing in versatile equipment ensures your manufacturing process can adapt to material changes and product evolution.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between plastic, aluminum, and laminated tube materials empowers you to make decisions aligned with your product, market, and sustainability goals. Plastic tubes offer affordability and versatility, aluminum tubes provide premium protection and longevity, and laminated tubes deliver a balanced solution combining multiple advantages.
As the packaging industry evolves, selecting the right material becomes increasingly important for product success and environmental responsibility. Whether you’re starting a new product line or optimizing existing packaging, evaluate your specific requirements against the unique benefits each material offers. Consider partnering with manufacturing experts who understand how to optimize your tube filling machine and production processes for your chosen material.
The right tube material isn’t just about meeting baseline requirements—it’s about creating value for your customers while maintaining operational efficiency and environmental stewardship.